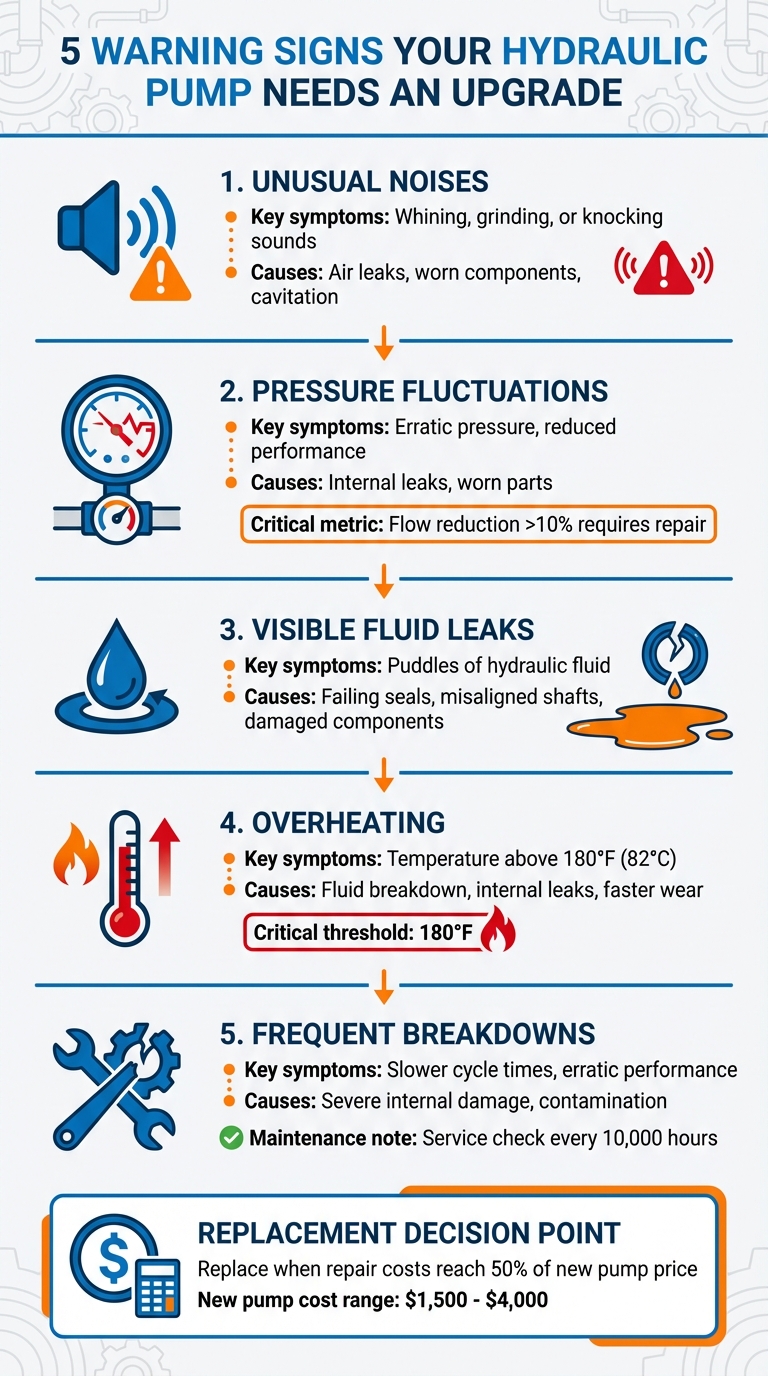
When your hydraulic pump starts showing signs of wear, ignoring the problem can lead to costly breakdowns and operational delays. Here are the top 5 warning signs that indicate it’s time to upgrade or replace your pump:
- Unusual Noises: Whining, grinding, or knocking sounds often point to air leaks, worn components, or cavitation.
- Pressure Fluctuations: Erratic pressure or reduced performance can signal internal leaks or worn parts.
- Visible Fluid Leaks: Puddles of hydraulic fluid typically mean failing seals, misaligned shafts, or damaged components.
- Overheating: Temperatures above 180°F cause fluid breakdown, internal leaks, and faster wear on parts.
- Frequent Breakdowns: Slower cycle times, erratic performance, and recurring failures suggest severe internal damage.
Ignoring these issues can result in system-wide damage, higher repair costs, and unplanned downtime. Regular maintenance, like monitoring case drain pressure or fluid temperature, can help prevent failures. If repair costs approach 50% of a new pump’s price (typically $1,500–$4,000), replacement is often the smarter choice.
For expert solutions, consider reaching out to professionals like NOVA Petroleum Services for diagnostics and high-quality pump upgrades.
5 Warning Signs Your Hydraulic Pump Needs Replacement
Hydraulics Troubleshooting and Testing
sbb-itb-325a090
1. Unusual Noises During Operation
Catching abnormal sounds early can save you from expensive system breakdowns. A hydraulic pump in good condition typically produces a steady hum. But if you hear a high-pitched whine, metallic grinding, or rhythmic knocking, it’s a red flag that something’s wrong and needs attention. These unusual noises often point to component wear and should be investigated further.
Physical Wear and Tear
Certain noises can reveal specific issues. A whining or squealing sound often means there’s cavitation or air entering the system through worn-out seals. Grinding noises, on the other hand, suggest severe mechanical wear, which can lead to metal debris contaminating valves, actuators, and seals. A rattling sound might indicate air entering the suction line. According to Final Drive Parts:
When a bearing finally fails and is not replaced, it can do serious damage if you keep trying to use the pump.
To confirm an air leak in the suction line, try squirting a little oil on the fittings. If the knocking sound pauses briefly, it’s likely an air infiltration issue.
Operational Efficiency Issues
These strange sounds don’t just signal physical damage – they can also disrupt system performance. Knocking noises caused by compressing air bubbles or worn bearings can destabilize fluid flow, leading to foaming and erratic actuator movements.
Impact on Maintenance Costs
Ignoring these auditory warning signs can result in system-wide contamination and skyrocketing repair costs. For instance, replacing a cylinder block might cost anywhere from $100 to $700, while bearings could be as cheap as $8. However, delaying repairs can lead to much higher expenses. Knowing what your pump normally sounds like makes it easier to spot subtle changes before they turn into major problems.
2. Pressure Fluctuations or Reduced Performance
If your pump’s pressure starts to fluctuate or its performance drops, it’s a clear sign of wear. Pressure fluctuations often show up as rhythmic movements on gauges or a noticeable decrease in output. These issues usually indicate internal wear that’s affecting the pump’s efficiency.
Physical Wear and Tear
Over time, components like gears, pistons, or vanes wear down, leading to internal leaks. These leaks create gaps that allow fluid to bypass the pressure side, reducing efficiency. A common symptom is the pressure gauge "hunting" or cycling rhythmically, which occurs when worn parts fail to maintain a proper seal during specific phases of operation. Mauricio Gomez, Director at DURAfilter Canada Inc., explains:
Flow reduction exceeding 10% indicates significant wear requiring hyd pump repair or replacement.
An early warning sign can often be found in the case drain line. Elevated pressure or flow in this line is a strong indicator of internal leaks. These leaks not only reduce pressure but also disrupt day-to-day operations.
Operational Efficiency Issues
Performance problems become evident during regular use. Equipment may respond sluggishly, cycle times may slow, and lifting capacity could noticeably decline. Internal leaks contribute to these issues and can also cause pressure gauge hunting. Operators often try to compensate by increasing RPM or pressure, but this only accelerates wear and tear. Additionally, the pump may draw more power to maintain pressure, which increases operational costs.
System Reliability and Performance
Other factors beyond wear can also destabilize pressure. Aeration, for instance, occurs when air enters the system, leading to foamy or milky fluid. This makes controls feel "spongy" and causes inconsistent pressure. Similarly, cavitation, which happens when low inlet pressure forms vapor bubbles, can result in erratic actuator movement and even metal erosion. Contaminated or faulty pilot valves may also cause sudden pressure spikes, damaging seals and other components. To prevent these problems from escalating, industry experts recommend a full service check after every 10,000 hours of operation.
Impact on Maintenance Costs
Pressure-related issues can quickly drive up maintenance expenses. Ignoring these problems often leads to severe internal leakage and excessive heat. If your pump operates at or above 180°F (82°C), it’s a sign of serious efficiency problems. High temperatures thin the oil, speeding up component wear and creating what technicians refer to as a "death spiral" of declining efficiency.
To stay ahead of these issues, consider installing digital pressure gauges with data logging. These tools can catch intermittent spikes that analog gauges might miss. Flow meter tests are another useful option, helping you measure output degradation before a complete failure occurs. If repair costs start to approach 50% of the price of a new pump – usually between $1,500 and $4,000 – it’s often more cost-effective to replace the pump altogether.
3. Visible Fluid Leaks
Spotting puddles of hydraulic fluid beneath your equipment is a clear warning sign that something’s wrong. These visible leaks are often caused by failed seals, gaskets, or fittings and can signal deeper mechanical problems. Even a minor drip can quickly escalate into significant downtime, costly repairs, and safety risks.
What you see on the outside is often just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to internal mechanical stress.
Physical Wear and Tear
Leaks commonly stem from worn-out or damaged components like shaft seals, O-rings, and gaskets. However, if you find yourself replacing seals repeatedly, the real issue might be a misaligned drive shaft. Misalignment puts uneven pressure on seals, causing them to fail prematurely. Other culprits include cracked housings, loose fittings, and damaged hoses. These external leaks don’t just waste fluid – they allow contaminants to enter the system, accelerating wear on internal parts like valves and pistons. Mauricio Gomez, Director at DURAfilter Canada Inc., explains:
The contamination entering through failed seals causes more damage than the leaked fluid volume suggests.
So, while leaks may seem like just a surface issue, they often lead to more severe internal damage over time.
The effects of leaks aren’t limited to physical damage – they also directly impact how efficiently your system operates.
Operational Efficiency Issues
Leaks undermine system performance by reducing pressure and flow, which forces the pump to work harder. This can result in slower cycle times, weaker lifting capabilities, and higher energy consumption. Additionally, as fluid levels drop, air can enter the system – a condition called aeration – leading to erratic actuator movements and loud banging noises. If fluid temperatures rise above 180°F (82°C) due to inefficiencies, the oil becomes thinner and oxidizes, worsening leaks and causing further seal damage.
Impact on Maintenance Costs
Leaks aren’t just messy – they’re expensive. Beyond the cost of wasted fluid, you may face environmental cleanup fees and even safety violation penalties. Frequent repairs, like replacing O-rings (which cost between $5 and $10 each), can add up quickly and may end up costing more than investing in a system upgrade. If repair expenses approach 50% of the cost of a new pump – which typically ranges from $1,500 to $4,000 – it’s probably time to consider a replacement.
To catch issues early, use infrared thermometers to check for hot spots near seals or valves, as these often indicate internal leaks before you notice external puddles. And if seals keep failing despite replacements, misaligned shafts are often the underlying problem. Addressing these root causes can save you from repeated headaches and unnecessary expenses down the road.
4. Overheating Components or Fluid
When a hydraulic pump operates at unsafe temperatures, the fluid inside begins to break down. Once temperatures exceed 180°F (82°C), the hydraulic fluid starts losing viscosity and oxidizing, which drastically shortens its lifespan.
Operational Efficiency Issues
When hydraulic fluid becomes too thin, internal leakage increases. This means the pump delivers less fluid with each revolution. Additionally, worn sealing surfaces allow fluid to bypass pressure circuits, which generates even more heat. This creates a self-perpetuating problem: the pump works harder to maintain pressure, producing more heat and further increasing leakage. The end result? Slower cycle times, reduced force output, and accelerated wear on the pump.
Physical Wear and Tear
Excessive heat damages the protective oil film that shields internal components. Bearings are particularly vulnerable – high temperatures can cause them to lose critical clearances and fail quickly. Seals, gaskets, and O-rings also suffer under prolonged heat exposure, becoming brittle, cracking, or tearing, which leads to leaks both inside and outside the system. Poor lubrication intensifies the damage, causing piston scoring, vane tip damage, and gear tooth wear. Tools like infrared thermometers or thermal imaging cameras can help detect localized hot spots before they lead to catastrophic failures. Just like unusual noises or sudden pressure changes, overheating accelerates internal damage and shortens the lifespan of your equipment.
System Reliability and Performance
An overheated system often results in erratic actuator movements. Overheated fluid can also cause cavitation, where vapor bubbles form and collapse violently, eroding metal surfaces and creating damaging vibrations. As the fluid oxidizes, varnish deposits may form, restricting flow and causing components to stick. According to industry data, 80% to 90% of hydraulic problems are linked to contamination, a condition often worsened by heat-induced fluid degradation. As Servo Kinetics explains:
At temperatures of 180°F or higher, hydraulic fluid begins to lose viscosity, reducing its lifespan.
Impact on Maintenance Costs
Overheating doesn’t just affect performance – it also drives up maintenance costs. Beyond the expense of replacement parts, unresolved overheating increases power consumption as the system works harder to maintain pressure. DURAfilter Canada highlights the financial risks, warning that ignoring early signs of overheating can lead to failures that halt operations for days, potentially costing tens of thousands of dollars in emergency repairs and lost production. Routine maintenance like fluid changes, system flushing to remove varnish, and replacing seals can quickly add up. In some cases, these costs approach the $1,500 to $4,000 price range of a full pump replacement. Monitoring case drain temperatures regularly can help detect excessive internal leakage early, reducing the risk of a total system breakdown.
If overheating continues to be an issue, upgrading your hydraulic pump could save you from escalating operational and maintenance costs. For expert guidance and quality upgrade options, reach out to NOVA Petroleum Services / Atokan Drilling Technologies Inc (https://novapservices.com).
5. Frequent Breakdowns or Slow Response Times
Frequent breakdowns or sluggish performance often point to serious internal problems. These issues not only disrupt operations but also signal that critical components within your system are wearing out, ultimately affecting its overall reliability.
Operational Efficiency Issues
One of the first signs of trouble is slower cycle times. If your equipment is taking longer to complete tasks it once handled with ease, it could mean that worn components are allowing fluid to bypass pressure zones. When the flow output drops below the manufacturer’s recommended levels due to extended wear, it’s a clear indication that repairs – or even a replacement – might be necessary. Trying to compensate by increasing RPMs or pressure might seem like a quick fix, but it only adds to fuel consumption and puts additional strain on other components. These inefficiencies are often tied to the physical deterioration highlighted below.
Physical Wear and Tear
Contaminated fluid is a major culprit behind pump wear. Dirt particles in the fluid act like abrasive sandpaper, grinding down pistons, gears, and bearings. Issues like cavitation and aeration worsen the problem, creating harmful metal debris that accelerates internal damage. Worn shaft seals exacerbate the situation by letting contaminants in and allowing fluid to leak out.
System Reliability and Performance
When a pump experiences significant internal wear, its performance becomes erratic. For example, fluctuating pressure gauges – often called "hunting" – and sluggish actuators are common warning signs. In variable displacement pumps, problems like contaminated pilot valves or worn control pistons can cause the pump to operate at a fixed output, regardless of what the system actually requires. These malfunctions can lead to dangerous pressure spikes, which risk damaging downstream valves and actuators.
Impact on Maintenance Costs
Frequent breakdowns don’t just disrupt operations – they also drive up repair expenses. Mauricio Gomez, Director at DURAfilter Canada Inc., puts it plainly:
Missing these early indicators leads to failures that shut down operations for days while costing tens of thousands in emergency repairs and lost production.
Metal debris from worn pump components can damage high-cost parts like valves and actuators. Plus, the extra energy consumption from an inefficient pump can end up costing more than investing in proactive maintenance. Once repair costs climb to 50% of a new pump’s price – usually between $1,500 and $4,000 – it’s often more economical to replace the pump entirely. Experts suggest performing comprehensive service checks every 10,000 hours of operation to catch problems early and avoid costly downtime.
Addressing these warning signs promptly can save you from catastrophic failures and protect the rest of your hydraulic system. Acting now ensures your system remains functional until you’re ready for a full upgrade. For expert advice on equipment upgrades or replacement options, visit NOVA Petroleum Services.
Conclusion
Identifying the warning signs of a failing pump is essential to avoid costly downtime and prevent equipment damage. Issues like unusual noises, pressure inconsistencies, visible leaks, overheating, and frequent breakdowns often point to underlying problems. If ignored, these problems can escalate into severe system failures, potentially halting operations for days and racking up significant expenses.
The risks of neglecting these signs are steep – emergency repairs, lost production, and damage to high-value downstream components can cost tens of thousands of dollars. Acting quickly when these symptoms arise can save both time and money.
Industry experts suggest scheduling service checks every 10,000 hours and replacing the pump when repair costs approach 50% of the price of a new unit, which typically ranges between $1,500 and $4,000. Upgrading to a new pump not only restores efficiency but also eliminates internal leaks and reduces energy consumption, improving overall performance.
For those considering upgrades or replacements, NOVA Petroleum Services provides comprehensive hydraulic pump solutions. Their team offers diagnostics, advice on repair versus replacement, and access to top-quality pumps from leading manufacturers across the USA, Canada, the UK, and the European Union.
FAQs
What happens if you ignore the warning signs of a failing hydraulic pump?
Ignoring the warning signs of a failing hydraulic pump can spell trouble for your operations. You might face increased wear and tear on system components, overheating issues, and even safety risks. On top of that, neglecting these problems often leads to unplanned downtime, expensive last-minute repairs, and major production setbacks.
Taking action early can make a big difference. It saves time, reduces costs, and keeps your system running smoothly and safely. Prioritizing regular maintenance and addressing upgrades when needed are key steps to sidestep these challenges.
How does regular maintenance help prevent hydraulic pump failures?
Regular upkeep plays a key role in avoiding expensive hydraulic pump failures by tackling problems before they spiral out of control. Routine inspections can uncover early warning signs like leaks (both internal and external), worn-out seals, or unusual noises. These issues, if ignored, can lead to pressure drops or fluid contamination. Checking fluid levels and its condition during service intervals is equally important – it helps prevent air from entering the system and stops cavitation, both of which can cause overheating and speed up wear and tear.
Essential maintenance tasks include cleaning or replacing filters, keeping an eye on overheating, and ensuring the pump’s flow and speed stay within recommended limits. For instance, overheating often points to internal wear or dirty fluid, and addressing it quickly can help avoid major damage. Staying on top of these tasks not only prevents sudden breakdowns but also reduces downtime and cuts down on costly emergency repairs.
For operators across the United States, partnering with a reliable supplier like NOVA Petroleum Services gives you access to high-quality replacement parts, expert guidance, and customized upgrade solutions – helping you keep your hydraulic system running smoothly and efficiently.
How do I know when it’s more cost-effective to replace a hydraulic pump rather than repair it?
Deciding whether to fix or replace a hydraulic pump comes down to a few key considerations: the severity of the damage, the cost of repairs, and how well the pump is performing overall. If the pump is breaking down often, running inefficiently, or nearing the end of its expected lifespan, replacing it could save money in the long run.
While repairs might seem like the cheaper route initially, repeated problems can quickly add up in terms of costs, lost productivity, and downtime. To make the most informed choice, it’s wise to weigh the total cost of ownership and seek advice from a professional.