Choke valves are essential for controlling wellhead pressure in oil and gas wells. They regulate fluid flow by creating a controlled pressure drop, ensuring safety and efficiency for downstream equipment like pipelines and separators. Here’s what you need to know:
- Purpose: They manage high reservoir pressures, prevent equipment damage, and stabilize production rates.
- How They Work: Fluids pass through a restricted orifice, dropping pressure while maintaining controlled flow.
- Types: Fixed chokes have a set orifice size, while adjustable chokes allow for real-time flow adjustments.
- Benefits: Protects equipment, reduces wear, and extends the lifespan of production systems.
- Challenges: Regular maintenance is required to prevent erosion and ensure performance.
Choke valves are a key component for safe and efficient oilfield operations, particularly in high-pressure environments. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance ensure reliable performance and long-term cost savings.
#18 Choke Performance | Artificial Lift
How Choke Valves Work
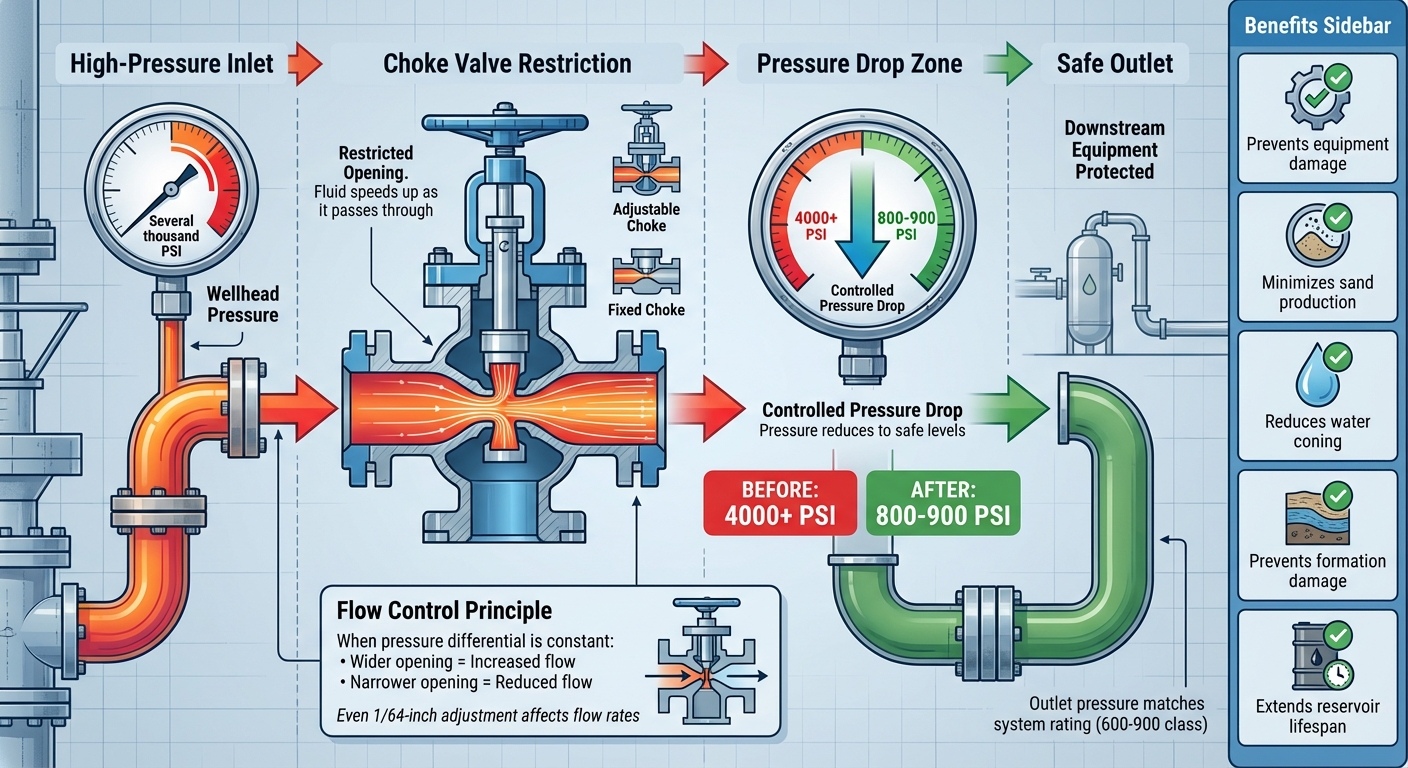
How Choke Valves Control Wellhead Pressure: A Step-by-Step Process
Flow Restriction and Pressure Control
Choke valves play a key role in managing wellhead pressure by forcing fluids through a restricted opening. As the fluid moves through this narrow passage, it speeds up, and its pressure drops. This controlled pressure drop at the Christmas tree ensures that downstream equipment operates safely, even when upstream wellhead pressure climbs to several thousand psi.
The connection between the choke opening and flow rate is simple: when the pressure differential is constant, opening the choke wider increases flow, while narrowing it reduces flow. Field teams use performance curves or sizing equations – based on valve Cv or Cd coefficients – provided by manufacturers to estimate how a specific adjustment, like changing the bean size or stem position, will influence production. For instance, even a small change, such as a 1/64-inch adjustment, can fine-tune flow rates (measured in barrels per day for liquids or thousand standard cubic feet per day for gas) while keeping pressures within safe limits for downstream systems.
This gradual pressure drop protects downstream equipment and reduces risks like erosion and reservoir damage. Controlled choking prevents a rapid drop in bottomhole pressure, which helps minimize sand production, water coning, and formation damage. This, in turn, extends the reservoir’s lifespan and stabilizes production over time. In high-pressure wells – where initial pressures can exceed several thousand psi but gathering systems are rated for lower pressures – the choke ensures the outlet pressure matches the system’s rating, such as a 600- or 900-class line.
Next, let’s explore the differences between adjustable and fixed chokes.
Adjustable vs. Fixed Chokes
Fixed choke valves use a fixed-diameter orifice, known as a bean, to regulate flow. In contrast, adjustable chokes feature a movable trim element – like a stem and needle, plug, or cage – that can be repositioned using a handwheel or actuator. This design allows operators to vary the flow area without needing to swap out hardware. Adjustable chokes offer a continuous range of flow adjustments, while fixed chokes provide specific capacity steps based on the bean size installed.
Adjustable chokes are especially useful during the early stages of a well’s life, cleanup, and testing, when production targets or operating conditions frequently shift. They enable operators to fine-tune flow and pressure in real time, often remotely or automatically, without shutting down the well. Once the well stabilizes and an optimal operating point is determined, many operators switch to a fixed choke with the appropriately sized bean. Fixed chokes have fewer moving parts, making them more durable and less likely to fail or be misadjusted – qualities that are particularly valuable in abrasive or hard-to-access environments.
In some setups, operators use both types together: an adjustable choke upstream for flexibility and a fixed choke downstream to simplify long-term operations. For equipment tailored to specific pressure, flow, and fluid conditions, operators can turn to NOVA Petroleum Services / Atokan Drilling Technologies Inc for reliable choke and wellhead solutions.
Types of Choke Valves
Choke valves come in various designs, each tailored to tackle specific production challenges. The three main types – fixed, adjustable, and bean-type – are commonly used to manage wellhead pressure, with each offering unique advantages depending on operational needs.
Fixed choke valves rely on a fixed orifice with a set diameter. The flow area remains constant unless the well is shut down, depressurized, and the choke insert or "bean" is replaced. These valves are built with durable bodies and trims made from carbide or alloy to withstand high erosion. They’re particularly suited for mature wells where reservoir pressure is stable, and production targets are steady. Operators often switch from adjustable to fixed chokes in such scenarios to minimize maintenance. This design reduces the number of moving parts, which is especially helpful for remote locations where servicing is more challenging.
Adjustable choke valves offer a more flexible approach, allowing the orifice opening to be adjusted externally using a handwheel or actuator. This continuous control over flow and pressure makes them ideal for early well life, cleanup operations, and testing – situations where reservoir pressure or production rates can change frequently. However, their more intricate design may require additional maintenance, particularly in abrasive environments.
Bean-type choke valves use replaceable inserts known as "beans", which can be installed in either a fixed or adjustable body. These beans come in standardized sizes and often feature hardened or carbide-lined bores to resist erosion. Changing the bean quickly alters the orifice size while maintaining a consistent flow coefficient. This simplifies well testing and production planning. For high-pressure wellheads, operators might pair an adjustable mechanism for fine-tuning with interchangeable beans for larger, predictable rate changes.
The choice between these valve types depends on factors like the well’s lifecycle, erosion risks, automation requirements, and how often operating conditions are expected to shift. Many operators in the U.S. start with an adjustable choke during the early, unstable flow phase. As conditions stabilize, they often transition to a fixed or bean-type choke to balance operational flexibility with simplicity and long-term durability.
sbb-itb-325a090
Using Choke Valves for Wellhead Pressure Management
Evaluating Wellhead Pressure Requirements
To manage wellhead pressure effectively, start by measuring reservoir, tubing, and casing pressures, along with the limits of downstream equipment. These measurements are key to determining the necessary pressure drop and ensuring proper valve selection and operation.
Next, establish your target production rate – whether it’s barrels per day for oil or thousand cubic feet per day for gas – and calculate the allowable pressure drawdown. Overdrawing the reservoir can lead to complications like sand production or water coning, so careful calculations are crucial. Use manufacturer sizing charts or software to find the choke orifice size that matches your desired flow rate, considering the measured upstream and downstream pressures. For gas wells, ensure you’re using API 6A-rated valves and confirm that outlet pressures align with downstream equipment ratings. Even in the event of a fully open choke failure, the wellhead pressure must remain within the rated working pressure of the downstream piping.
Once you’ve defined these pressure requirements, you can move forward with selecting and installing the appropriate choke valve.
Selecting and Installing Choke Valves
Choose a fixed choke for wells with stable flow conditions or an adjustable choke for start-up phases or wells with variable production. Ensure the valve’s pressure rating and material specifications align with your well’s conditions, including factors like sour versus sweet service and temperature ratings, as outlined in API 6A standards. Proper installation is essential to support long-term maintenance and performance.
Pay attention to installation orientation. Surface choke valves are typically mounted with side-entry flow rather than vertically, as this setup simplifies maintenance and improves control. Be sure to include upstream and downstream block valves for isolation, as well as bleed-off points to safely depressurize the system before maintenance. Clear access for replacing components like beans or trims is also critical. For automated chokes, confirm the control logic (fail-open or fail-closed), power supply, and integration with SCADA or DCS systems. Operators looking for equipment or technical support can contact NOVA Petroleum Services / Atokan Drilling Technologies Inc for assistance with installation, upgrades, and renewals.
Monitoring and Maintaining Choke Valves
After installation, maintain optimal valve performance by setting up inspection routines based on the severity of operating conditions. For wells in high-erosion environments, inspect sealing surfaces, check for cage and plug wear, and monitor vibration every few weeks. For less demanding conditions, quarterly inspections may be sufficient. Regular maintenance tasks include replacing worn throttle beans, lubricating adjustable components, flushing out debris, and inspecting actuators to prevent failures.
Train operators to identify early warning signs of problems. Sudden shifts in downstream pressure or flow, high-pitched jetting noises, or difficulty moving the stem can all indicate developing issues. Keeping spare trims and beans on hand for critical wells can reduce downtime and avoid costly delays. Additionally, recording choke settings alongside production data over time can help refine schedules as reservoir pressure declines naturally. Routine maintenance not only extends the life of the equipment but also ensures smooth production – especially important for remote locations where service calls can be expensive and time-consuming.
Benefits and Challenges of Choke Valves
Benefits of Choke Valves
Choke valves play a crucial role in maintaining control over flow rates and pressure, ensuring wellhead conditions remain within safe limits while maximizing production efficiency. By dissipating energy, these valves help prevent equipment failures like ruptures, leaks, and blowouts. This staged pressure reduction also minimizes hydraulic shocks and vibrations during flow changes, leading to smoother operations and reducing wear on downstream components like separators, meters, and pipelines.
Another key advantage is their ability to extend the lifespan of equipment. By managing where pressure drops occur, choke valves keep fluid velocities in a safer range, protecting both the valve itself and downstream systems. This controlled throttling is especially important in high-pressure wells, where stress on equipment is more pronounced. Over time, this can delay the need for costly repairs or replacements, making choke valves a cost-effective solution for demanding environments.
While these benefits are significant, choke valves also come with their share of challenges.
Challenges in Using Choke Valves
Despite their advantages, choke valves can face several operational hurdles. One major concern is erosion and material wear, particularly in high-pressure and high-velocity applications. Small channel areas and high fluid speeds can lead to seal damage and vibrations, accelerating wear and tear. Additionally, large pressure drops in a single stage can cause cavitation and noise, often requiring the use of specialized multi-stage trims and durable materials like tungsten carbide.
To address these issues, operators must commit to regular inspections and timely part replacements. In harsh service conditions, trims, seats, and orifices need frequent checks to prevent blockages or excessive wear. While this proactive maintenance increases labor and material costs, it helps avoid severe equipment failures and unplanned downtime.
Another challenge lies in choosing between fixed and adjustable choke valves. Fixed chokes are simpler and more robust but lack the flexibility to adapt to changing conditions. On the other hand, adjustable chokes provide precise control over flow and pressure but feature more intricate internals that are more susceptible to erosion and require greater maintenance.
Comparison Table: Benefits vs. Limitations
| Aspect | Benefit of Choke Valves | Limitation / Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Control | Ensures precise control of wellhead and downstream pressure | Risk of erosion with high-pressure drops in small openings |
| Safety | Protects pipelines and surface equipment from overpressure | Improper operation or failure can compromise safety |
| Equipment Life | Reduces wear on downstream systems like piping and instruments | Requires regular maintenance and part replacements |
| Production Optimization | Stabilizes flow, reducing surges and slugging | Needs careful tuning to avoid potential reservoir damage |
| Operational Flexibility | Adjustable chokes allow fine-tuning as conditions change | Complex internals demand more frequent maintenance |
Conclusion
Choke valves play a vital role in managing wellhead pressure by introducing a controlled flow restriction. This process reduces pressure and safeguards downstream equipment. By adjusting the valve’s opening, operators can maintain desired pressures, prevent surges, and protect critical infrastructure like separators, pipelines, and surface facilities. This level of control is essential throughout the entire lifecycle of a well.
As a well matures, the choke settings are adjusted to adapt to changing conditions. During the high-pressure startup phase, the valve remains tightly controlled. Over time, as reservoir pressure declines, the valve is opened further to sustain stable production. This adaptability ensures that economic flow rates are maintained, even as factors like water cut or the gas/oil ratio evolve.
When properly sized and maintained, choke valves offer several operational advantages. They stabilize production rates to match facility capacity, regulate reservoir drawdown to delay water or gas breakthroughs, and minimize wear on equipment. These benefits help reduce maintenance costs and extend the life of production systems. Routine maintenance and careful sizing, as highlighted earlier, are critical to achieving these outcomes. For field and production engineers, investing in appropriate choke sizing, trim selection, and regular inspections often leads to fewer failures, steadier production, and lower overall costs.
Specialized suppliers like NOVA Petroleum Services / Atokan Drilling Technologies Inc provide operators with tailored choke valve solutions. These include severe-service trims designed to handle high differential pressures and erosive conditions. Their expertise ensures that choke valves are matched to specific wellhead pressures, flow rates, fluid properties, and facility limits. Additionally, they assist with equipment upgrades, replacements, and renewals as wells age and operating conditions change.
FAQs
What is the difference between fixed and adjustable choke valves?
Fixed choke valves feature a set orifice size, ensuring consistent flow rate and pressure control. They work well in scenarios where stable, unchanging performance is necessary.
In contrast, adjustable choke valves let operators manually or automatically modify the orifice size, offering greater flexibility to manage wellhead pressure as conditions evolve. This makes them a better fit for situations that demand precision and the ability to adapt to shifting operational needs.
How do choke valves help protect equipment and extend its lifespan?
Choke valves are essential for safeguarding equipment and prolonging its service life by precisely managing flow rates and pressure. By slowing down fluid velocity, they help reduce the chance of high-speed impacts that could damage valve components and nearby equipment.
Additionally, controlling pressure effectively helps to avoid turbulence and cavitation – two common culprits behind erosion. This not only protects the valve itself but also preserves the wellhead systems, ensuring safer and more efficient operations in the long run.
What should you consider when choosing a choke valve for a wellhead?
When choosing a choke valve for a wellhead, there are several critical aspects to consider to ensure operations run smoothly and safely. Start by looking at the well pressure and flow rate – these factors will dictate whether the valve can handle your system’s specific demands. It’s also essential to evaluate the pressure control requirements to ensure the valve maintains consistent performance, even when conditions fluctuate.
Next, verify the valve size and pressure rating to ensure it aligns with your system’s specifications. Pay attention to the type of well fluids the valve will encounter, whether it’s oil, gas, water, or fluids with abrasive particles, as this can affect the valve’s performance and durability. Lastly, think about the operating environment, including temperature extremes and potential corrosion risks, and confirm the valve complies with all relevant safety standards for your setup.